在现代生物科技领域,crispr-cas9技术已经成为最受欢迎的基因编辑工具之一。
这种技术可以用来研究基因功能,疾病诊断和治疗等方面。其中最常用的应用就是构建基因敲除细胞模型。
本文将介绍crispr技术的基本原理和操作流程,以帮助您更好地了解和使用这种重要的基因编辑工具。

一、crispr技术的基础原理
crispr(clustered
regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)技术最初是从大肠杆菌中发现的一种天然的细菌防御系统,后来被发现可以被用于基因编辑。
crispr-cas9技术基于一种叫做“rna导向”的机制(guide rna, grna),这种机制可以让crispr-cas9系统选择性地识别和切割dna中的特定序列。这意味着我们可以使用crispr-cas9来精确地编辑细胞中的基因序列,包括基因敲除、插入、替换等等。
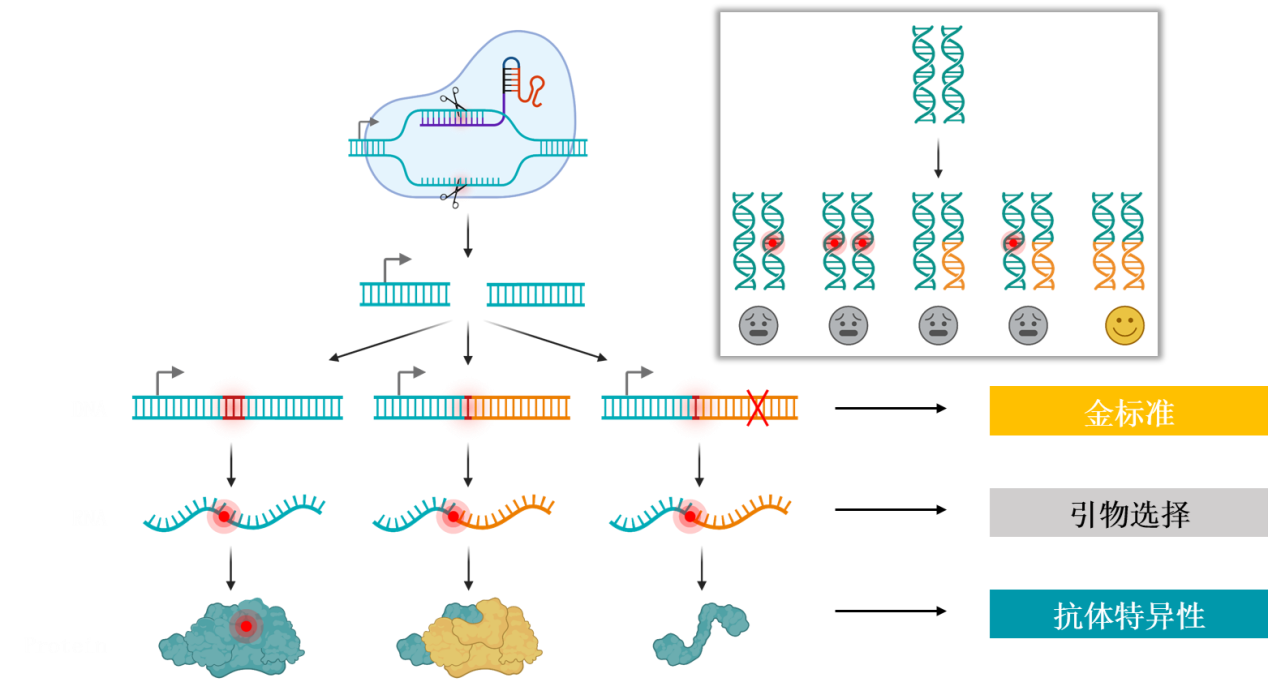
二、操作流程
crispr-cas9技术的操作流程分为四个主要步骤:设计grna、构建质粒、转染细胞、鉴定细胞。
1.
设计grna:grna是由crispr-cas9系统识别并切割目标dna的关键部分。我们需要在目标基因中选择一个合适的靶点序列,设计grna来引导cas9蛋白识别并切割该序列。
耐思开发的quick-ko?基因敲除试剂盒根据已知的人和小鼠编码基因,采用优化的预设计方案,相较于传统方案具有更高的敲除效率。
2.
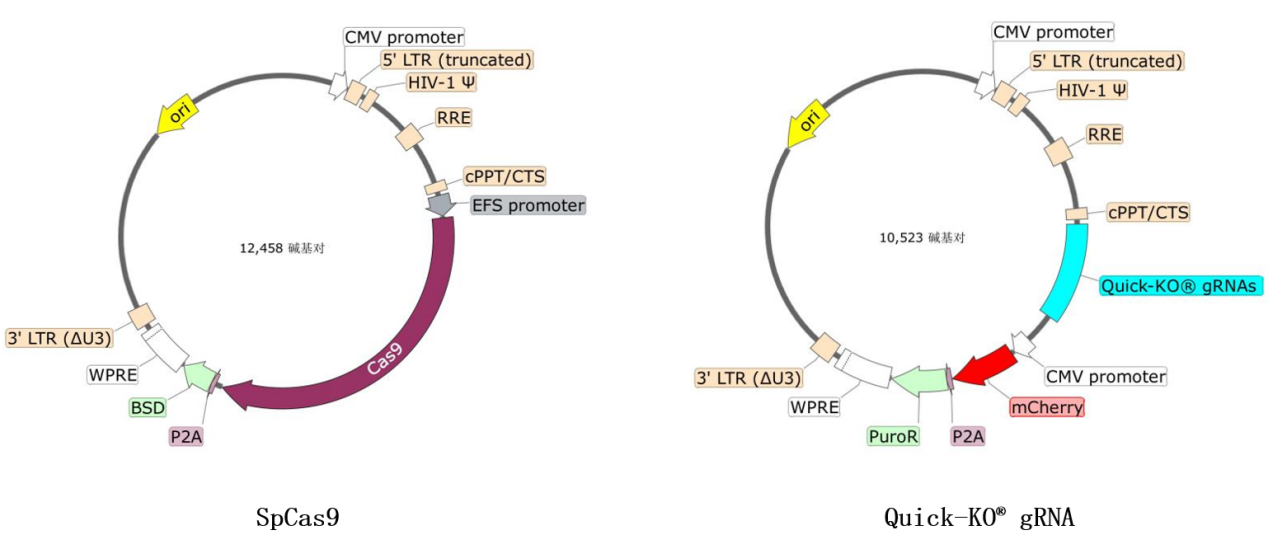
构建质粒:质粒是携带crispr-cas9系统和grna的载体。在构建质粒时,我们需要将cas9基因和grna序列克隆到质粒中,并确保它们可以在细胞中稳定表达。
耐思quick-ko?基因敲除试剂盒中的cas9质粒和grna质粒分别携带blasticidin和puromycin/mcherry筛选标记,方便用户进行阳性细胞富集。
3.
转染细胞:将质粒转染到目标细胞中,让它们表达crispr-cas9系统并编辑目标基因。转染可以通过电穿孔或者化学转染的方法进行。
此外,针对转染效率低的细胞,也可以选择耐思慢病毒款的quick-ko?基因敲除试剂盒。
4.鉴定细胞:最后一步是对成功转染的细胞进行筛选,通过pcr和测序的方法,筛选出具有目标基因敲除的细胞。
三、目标细胞类型
crispr技术可以用于多种细胞类型的编辑,包括哺乳动物细胞、酵母菌、昆虫细胞和植物细胞等。
其中,人类细胞是最常用的细胞模型之一,可以用于疾病模型的构建、药物筛选和基础研究等方面。
耐思quick-ko?基因敲除试剂盒主要针对人类细胞、小鼠细胞等哺乳动物细胞开发。

对于不同的目标细胞类型,我们需要根据细胞的特点和crispr技术的限制来选择合适的crispr-cas9系统和转染方法。
四、总结
基因敲除细胞模型的构建对于基础研究和药物研发等领域具有重要的意义。crispr技术的出现为基因编辑提供了一种高效、精准和经济的方法。在使用crispr-cas9技术进行基因敲除时,我们需要选择合适的grna和基因递送方法,最终获得目标基因敲除的细胞模型。
|
细胞 |
种属 |
组织/疾病 |
试剂盒方案 |
|
|
质粒型 |
慢病毒型 |
|||
|
22rv1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
prostate |
|
? |
|
293t |
homo sapiens (human) |
kidney; embryo |
? |
? |
|
4t1 |
mus musculus (mouse) |
breast; mammary gland |
|
? |
|
a2780 |
homo sapiens (human) |
ovary |
|
? |
|
a-549 |
homo sapiens (human) |
lung |
? |
? |
|
ags |
homo sapiens (human) |
stomach |
? |
|
|
aml12 |
mus musculus (mouse) |
liver |
|
? |
|
beas-2b |
homo sapiens (human) |
bronchus; epithelium |
|
? |
|
bon-1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
pancreas |
? |
|
|
c3h10t1/2 |
mus musculus (mouse) |
embryo |
|
? |
|
cfpac-1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
pancreas |
? |
? |
|
du145 |
homo sapiens (human) |
prostate |
|
? |
|
gist-t1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
gastrointestinal stromal tumor |
|
? |
|
hacat |
homo sapiens (human) |
back; skin; epidermis |
|
? |
|
hcc1395 |
homo sapiens (human) |
breast; duct; mammary gland |
? |
? |
|
hela |
homo sapiens (human) |
uterus; cervix |
? |
? |
|
hep3b |
homo sapiens (human) |
pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma |
? |
? |
|
hepa 1-6 |
mus musculus (mouse) |
liver |
|
? |
|
hepg2 |
homo sapiens (human) |
liver |
? |
? |
|
hl-60 |
homo sapiens (human) |
peripheral blood |
? |
? |
|
hmc-1.1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
mast cell leukemia |
|
? |
|
ht-29 |
homo sapiens (human) |
colon adenocarcinoma |
? |
? |
|
huh-7 |
homo sapiens (human) |
liver, gallbladder |
|
? |
|
huvec |
homo sapiens (human) |
umbilical vein |
|
? |
|
img |
mus musculus (mouse) |
brain |
|
? |
|
ipec-j2 |
sus scrofa (pig) |
small intestine; jejunum |
|
? |
|
jurkat |
homo sapiens (human) |
peripheral blood |
? |
? |
|
k-562 |
homo sapiens (human) |
bone; marrow |
? |
? |
|
km12-sm |
homo sapiens (human) |
colon carcinoma |
|
? |
|
lovo |
homo sapiens (human) |
colon adenocarcinoma |
|
? |
|
mda-mb-231 |
homo sapiens (human) |
breast adenocarcinoma |
|
? |
|
meg-01 |
homo sapiens (human) |
bone marrow |
|
? |
|
mimcd-3 |
mus musculus (mouse) |
kidney; inner medullary collecting duct |
? |
? |
|
mtec1 |
mus musculus (mouse) |
thymus |
|
? |
|
mcf-7 |
homo sapiens (human) |
invasive breast carcinoma |
|
? |
|
nih 3t3 |
mus musculus (mouse) |
whole embryo |
|
? |
|
panc-1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
pancreas; duct |
|
? |
|
pc-3 |
homo sapiens (human) |
prostate |
|
? |
|
qgp-1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
pancreas; islets of langerhans |
? |
? |
|
sgc-7901 |
homo sapiens (human) |
uterus; cervix |
|
? |
|
sh-sy5y |
homo sapiens (human) |
neuroblastoma |
? |
? |
|
sk-hep-1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
liver; ascites |
? |
? |
|
snu-1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
stomach |
? |
? |
|
sw480 |
homo sapiens (human) |
large intestine; colon |
|
? |
|
t-47d |
homo sapiens (human) |
breast; mammary gland |
|
? |
|
thp-1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
peripheral blood |
|
? |
|
u-87mg |
homo sapiens (human) |
brain |
|
? |
|
um-uc-3 |
homo sapiens (human) |
urinary bladder |
|
? |
|
ws1 |
homo sapiens (human) |
skin |
? |
? |
|
ct26 |
mus musculus (mouse) |
colon |
|
? |
